New Publication
The effect of landmark visualization in mobile maps on brain activity during navigation: A virtual reality study
Front. Virtual Real., 15 November 2022
Cheng, B., Wunderlich, A., Gramann, K., Lin, E., & Fabrikant, S. I
Abstract
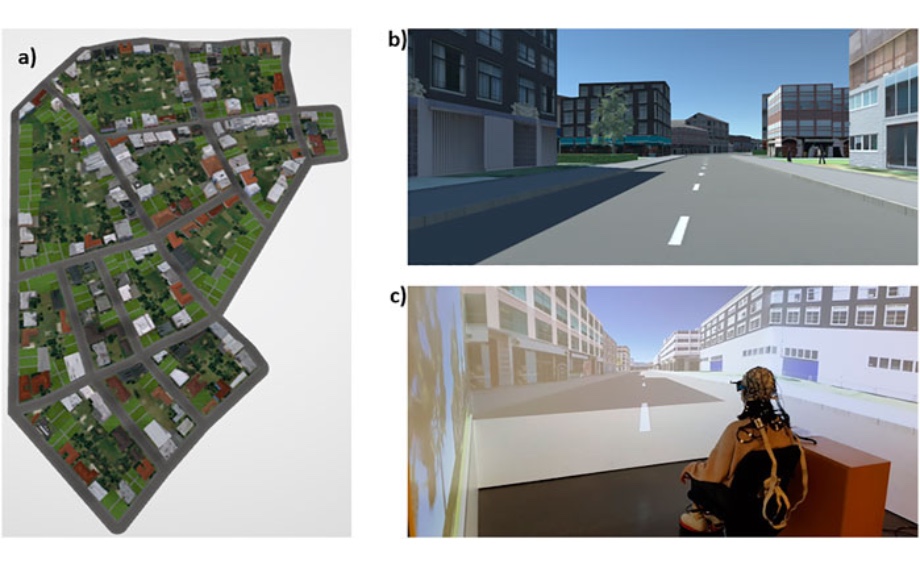
The frequent use of GPS-based navigation assistance is found to negatively affect spatial learning. Displaying landmarks effectively while providing wayfinding instructions on such services could facilitate spatial learning because landmarks help navigators to structure and learn an environment by serving as cognitive anchors. However, simply adding landmarks on mobile maps may tax additional cognitive resources and thus adversely affect cognitive load in mobile map users during navigation. To address this potential issue, we set up the present study experimentally to investigate how the number of landmarks (i.e., 3 vs. 5 vs. 7 landmarks), displayed on a mobile map one at a time at intersections during turn-by-turn instructions, affects spatial learning, cognitive load, and visuospatial encoding during map consultation in a virtual urban environment. Spatial learning of the environment was measured using a landmark recognition test, a route direction test, and Judgements of Relative Directions (JRDs). Cognitive load and visuospatial encoding were assessed using electroencephalography (EEG) by analyzing power modulations in distinct frequency bands as well as peak amplitudes of event-related brain potentials (ERPs). Behavioral results demonstrate that landmark and route learning improve when the number of landmarks shown on a mobile map increases from three to five, but that there is no further benefit in spatial learning when depicting seven landmarks. EEG analyses show that relative theta power at fronto-central leads and P3 amplitudes at parieto-occipital leads increase in the seven-landmark condition compared to the three- and five-landmark conditions, likely indicating an increase in cognitive load in the seven-landmark condition. Visuospatial encoding indicated by greater theta ERS and alpha ERD at occipital leads with a greater number of landmarks on mobile maps. We conclude that the number of landmarks visualized when following a route can support spatial learning during map-assisted navigation but with a potential boundary—visualizing landmarks on maps benefits users’ spatial learning only when the number of visualized landmarks shown does not exceed users’ cognitive capacity. These results shed more light on neuronal correlates underlying cognitive load and visuospatial encoding during spatial learning in map-assisted navigation. Our findings also contribute to the design of neuro-adaptive landmark visualization for mobile navigation aids that aim to adapt to users’ cognitive load to optimize their spatial learning in real time.