#50: Why do we create virtual forests?
Combining 3d measurements and radiative transfer models helps to improve forest monitoring and to increase understanding of ecosystem functioning.
Given the increased pressure on forests and their diversity in the context of global change, new ways of monitoring diversity are needed. A set of globally relevant and consistent variables has been defined and been named essential biodiversity variables (EBVs), analogous to the essential climate variables (ECVs). Remote sensing has the potential to inform these variables on the global scale, but validation of data and products, particularly in remote areas, is difficult. We have developed an approach using radiative transfer models, parameterised with a detailed 3d forest reconstruction based on laser scanning, that can be used to test and validate information retrieval from remote sensing, purely in the virtual domain.
3d remote sensing technologies providing forest structure information
For the 3d reconstruction of the vegetation canopy needed in our models, we use laser scanning across a range of scales. This technology enables us to reconstruct trees with branches if we use close-range laser scanning (either from the ground or from drones) and the location of trees in the landscape if we use laser scanning from airborne platforms. In addition, it provides a direct source of so-called morphological traits, which are as well relevant in the context of EBV retrieval, as shown in a very recent paper, to which we contributed .
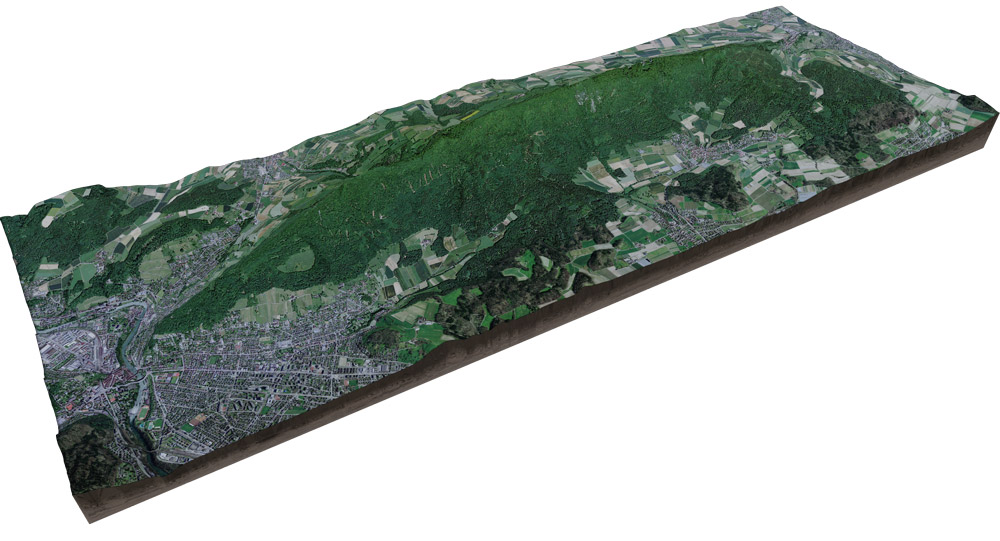
Our main site for developing this approach is the Lägern mountain range, with the core site being around the flux tower of ETH/WSL. An exemplary dataset acquired by terrestrial laser scanner on the site can be explored in full 3d.
Such datasets look impressive, but are merely a collection of coloured 3d points, albeit a lot of them. Consequently, a large part of our research is to develop automated methods that convert the devoid-of-semantics point cloud to meaningful information. Such information, e.g. tree location or branch geometry can then be used to construct a virtual representation of the forest.
3d ray tracing - understanding the light regime in forest canopies
We then use this 3d representation in so-called radiative transfer models or ray-tracers, which simulate the light regime within the complex 3d forest canopy. We currently use these models two-fold:
i) to simulate other remote sensing datasets (e.g. satellite images) and to test information retrieval methods on those, as we know all details of our virtual forest and
ii) to increase our understanding on how structure and the light regime are linked to forest functioning.
The Laegeren site image and the virtual forest stand were created the open-source raytracing tool 'blender'.
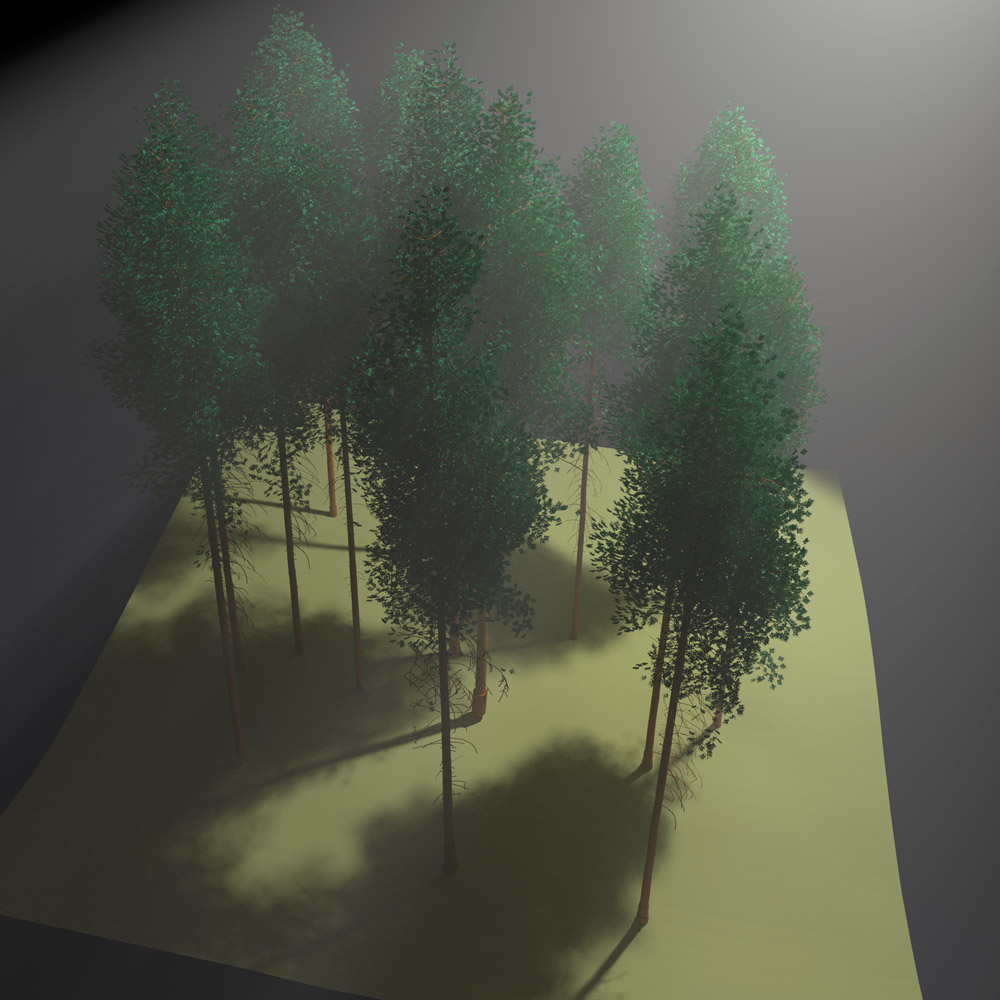
Concluding, such RT modelling frameworks have the potential to prototype and validate future space-borne observation concepts that are aimed at informing variables of biodiversity, while the 3d remote sensing based morphological traits could complement other observational approaches and in-situ networks of diversity, providing effective spatiotemporal gap filling for a comprehensive assessment of changes in diversity.
Felix Morsdorf


