#31: Unpacking the complexity of social-ecological systems
Systems thinking aims at breaking down social-ecological systems into the individual components and their interactions. Qualitative and quantitative models help to understand their dynamics.

Humans depend on natural resources, including fisheries, livestock grazing, forests and fresh water reservoirs. With a growing human population and a suite of environmental changes unfolding relatively rapidly, understanding how to use natural resources in a sustainable manner is of critical importance. These natural resources are part of complex social-ecological systems.
Interactions between resource users and the resource itself
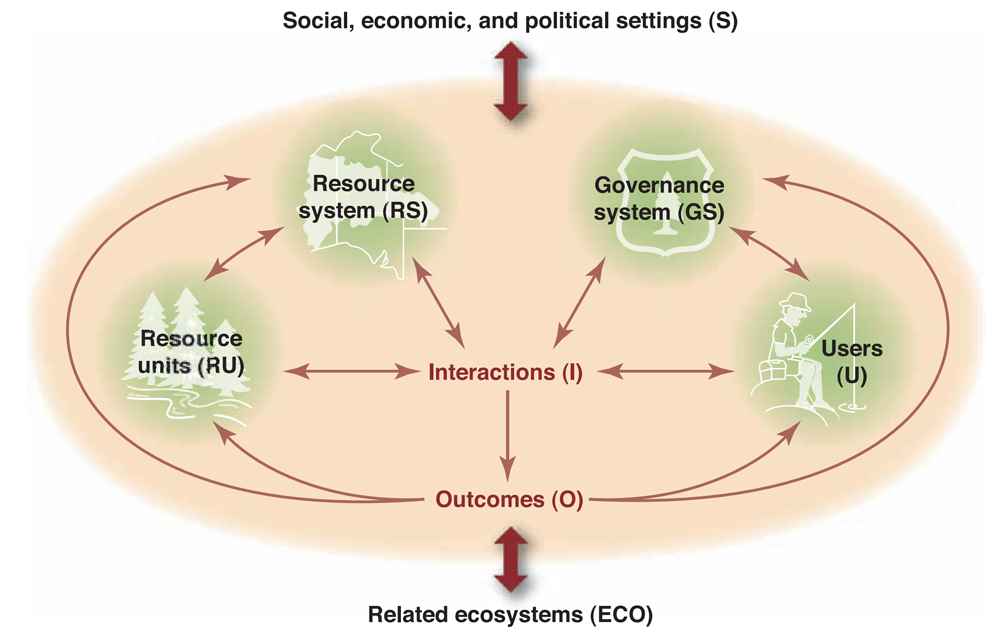
Social-ecological systems thinking provides a means to analyze interactions between resource users (i.e. humans) and the resource itself. In these systems, complexity arises from interactions taking place at different levels of organization. For example, the actions of individual foresters may be constrained by the rules and regulations set by the governance system.
Qualitative and quantitative models
To unpack this complexity, systems thinking aims to decompose social-ecological systems into its separate components, and the interactions that occur between these components. The result is a stylized or model description of the social-ecological system. These models can be studied qualitatively, by describing positive and negative interactions between components. They help to identify for example stabilizing and destabilizing feedbacks that can emerge in the social-ecological system.
Alternatively, interactions between components can be described quantitatively, by mathematical equations. With these we can study for example different scenarios for the future, and how these would impact the dynamics of the social-ecological system. Modelling can be an iterative process, where components of the system can be further decomposed into multiple smaller components, adding more detail to the model description. In this way, knowledge of the system can be gathered in a step-wise manner.
Sustainable management of common pool resources
How do communities share the use of a natural resource that can be accessed by multiple actors? Which networks of social-ecological interactions allow for sustainable management of such common pool resources? In the Earth System Science lab, these questions are pursued theoretically using the quantitative models described above. In addition, we conduct empirical work, using data on network interactions from fisheries and forestry systems. By comparing different types of social-ecological systems, we aim to disentangle general mechanisms that promote their sustainability and context-specific factors that may mediate system dynamics.
Maarten Eppinga