#115: Counting snowflakes from space
Do you like being active in the mountains? Are you a winter sports enthusiast? Or do you want to know how global warming affects water resources in Switzerland? Then you should have a look at the snow maps provided by ExoLabs, which are among the most accurate on the market.

ExoLabs is a spin-off from the Remote Sensing Laboratories @ GIUZ/UZH. Founded in 2017, it started with an innovative approach to map snow for the tourism market. Later, projects for insurances and federal offices followed. All projects have something in common: they are based on Earth observation (EO) data and the methods and algorithms used meet the highest scientific standards. Short: Science as a service. And this is also the motto of ExoLabs.
From science to business
Even if managing the scientific challenges is crucial to provide quality products and gain thrust in the community, mastering the financial challenges of a spin-off requires a different skillset. Winning customers in this area is not easy - especially if you lack a longstanding reputation. Therefore, the ExoLabs Team started from scratch by writing proposals and raising project funds from trusted entities. By now, they acquired grants from the European Space Agency, Innosuisse, the Swiss Space Centre and the European Union. This financial support enabled the further development of the products and to define a go-to-market strategy to win customers. And this has now been achieved this year, with first customers from the tourism and hydropower sectors. Although it is still a long way to go, the first steps have been taken.
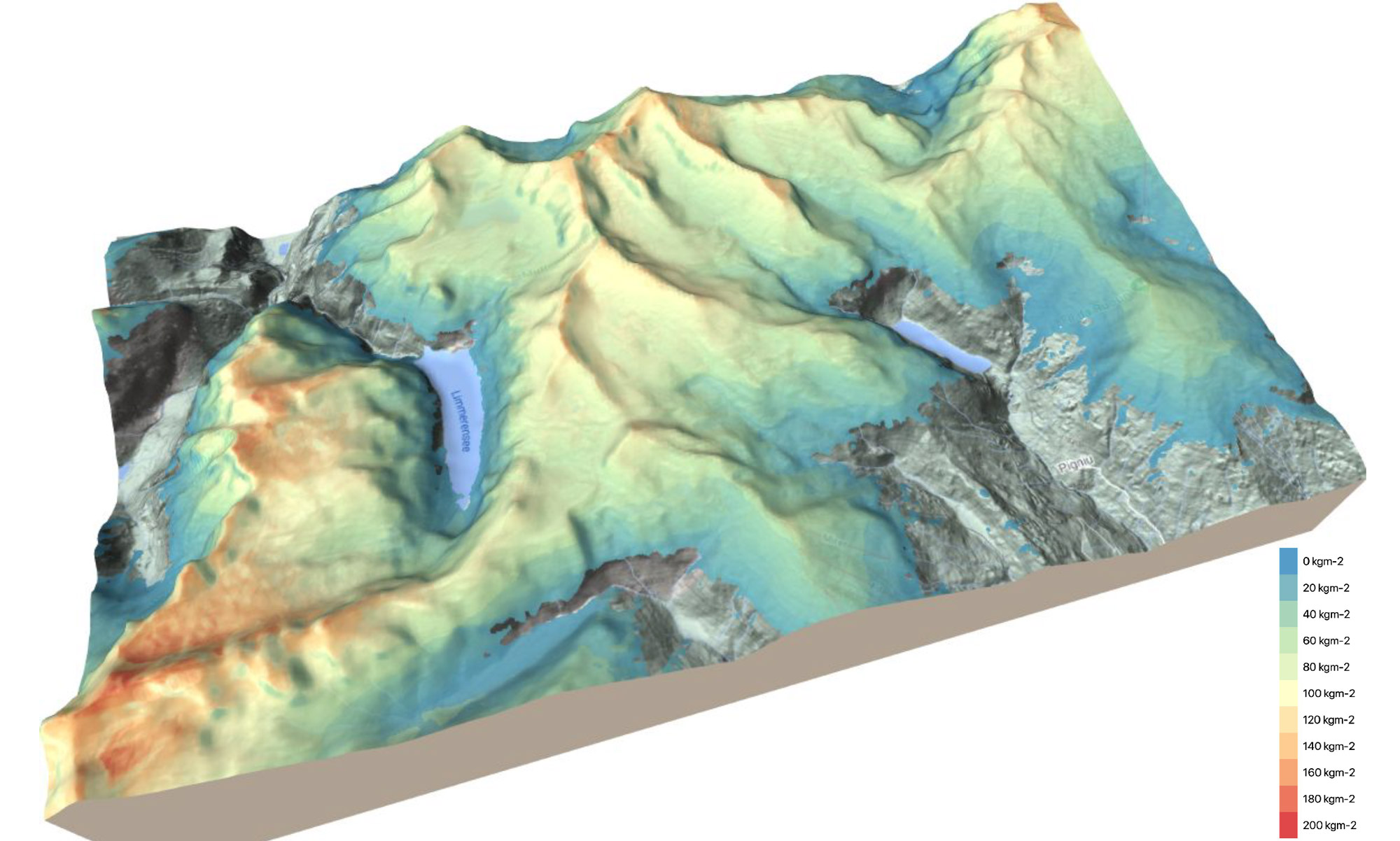
Snow mapping - still a challenge
Snow is one of the so-called Essential Climate Variables (ECVs) and thus contributes significantly to the characterization of the climate and related changes. The variable snow can be further differentiated into the variables snow cover, snow height and snow water equivalent (SWE). The precise detection and characterization of those variables, however, is a major challenge due to their high temporal and spatial variability. This variability can only be reproduced to a limited extent with the existing approaches - whether in terms of spatial detail accuracy, the timeliness of the measurements or the reflection of topographic variations. In Switzerland, for example, the Institute of Snow and Avalanche Research (SLF) publishes snow depth maps approximately once per week in a 1 km spatial resolution.
Snow mapping 2.0
The snow portfolio offered by ExoLabs are based on acquisitions from several satellite missions and contains snow cover, snow depth and snow water equivalent for entire mountain ranges. The product development is supported, supplemented, and evaluated by data of in-situ monitoring networks, modelled weather data and additional information about topography, radiation balance and land cover. At the heart of all these products lies an automated workflow enabling a daily and spatially detailed (20x20 meters) monitoring of the snow package based on state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms. Being aware of our limitations, we collaborate with research partners at ETHZ and the WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research SLF as well as with industry partners such as UBIMET and MetGIS (weather forecasts, Austria) or Think Outside (snow measuring equipment, Norway).
Snow for all
Although ExoLabs follows a classic business-to-business model, the visualization of the snow maps is still free of charge for every winter sports enthusiast. Have a look at our "ExoSnow" app - or use these snow maps in your next tour planning on the MountaiNow or Skitourenguru platforms. Have fun!
Hendrik Wulf, Reik Leiterer, Gillian Milani, Bernhard Sassik