#90: Mapping functional diversity from space
Global change and the loss of biodiversity threaten ecosystems around the world. Satellites provide continuous data on a global scale. A master thesis investigated the potential to assess functional diversity with satellite data at the Laegern forest.
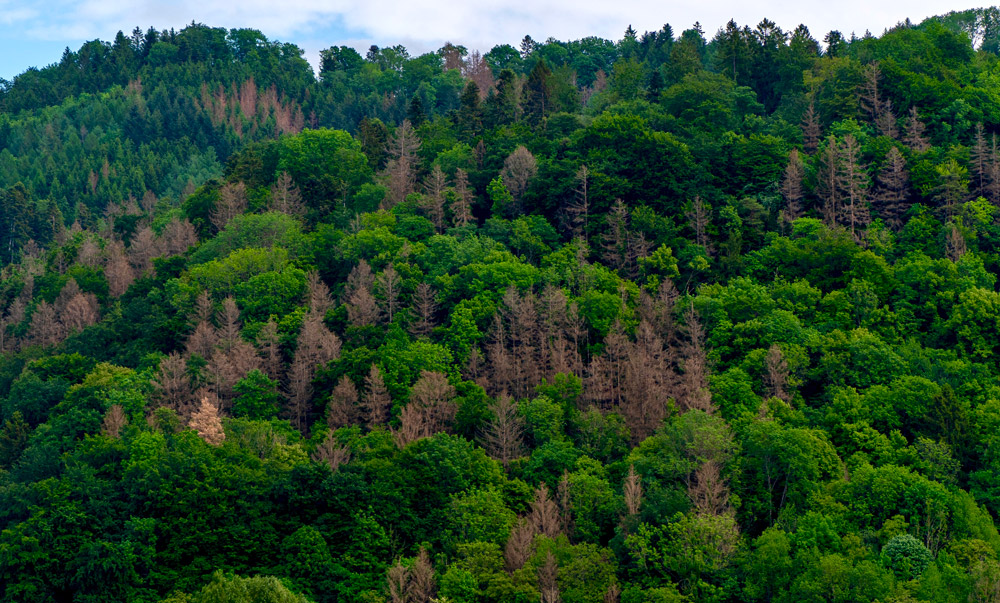

Biodiversity is declining worldwide, which makes ecosystems more vulnerable to disasters and diseases. Halting biodiversity loss and reducing its effects are goals for sustainable development of international interest.
Biodiversity is not only defined by species richness. Functional diversity of plant traits, e.g., their height or the pigment content of their leaves, is also relevant for ecosystem stability and health. We measure traits from a distance by recording the sunlight reflected by the plant. From this, biochemical properties can be deduced, such as their chlorophyll or water content.
From aerial photographs to satellite-based systems
In my master thesis, I transferred an existing method for measuring the functional diversity from airborne to spaceborne data. My study area was the forest on the Laegern, a mountain northwest of Zurich, which you can see from the Irchel campus.
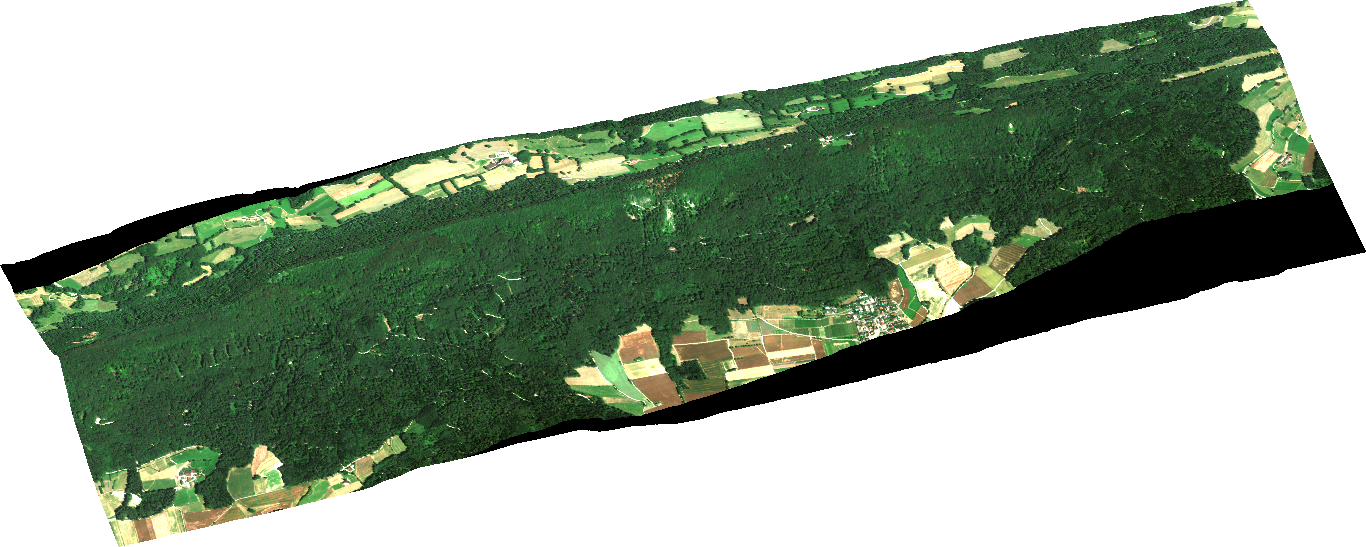
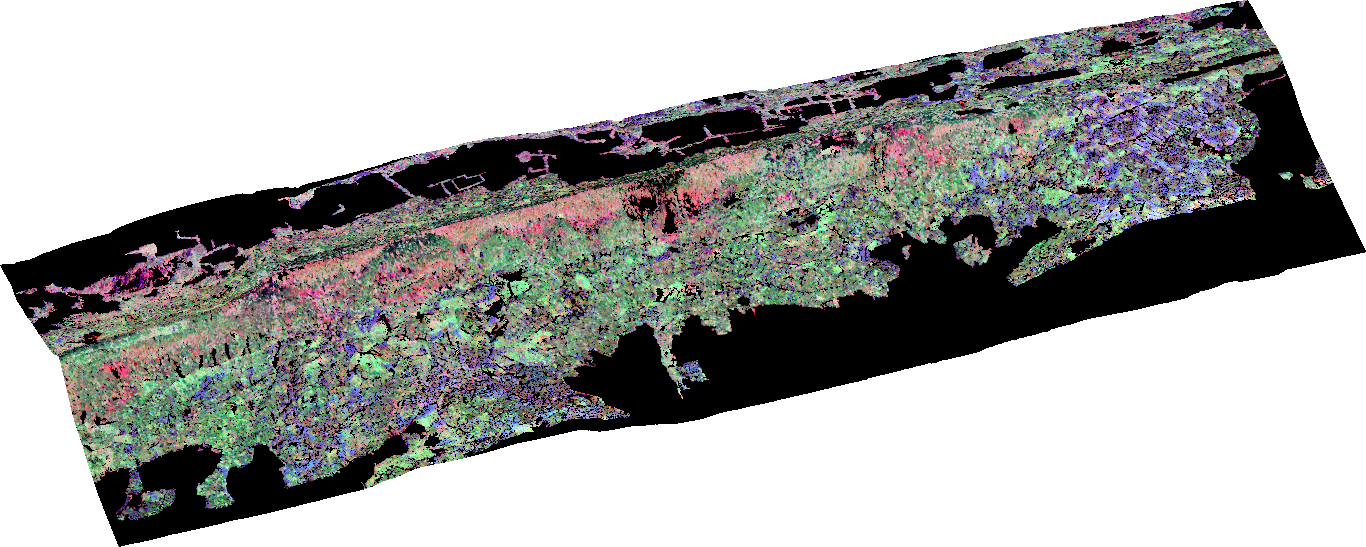
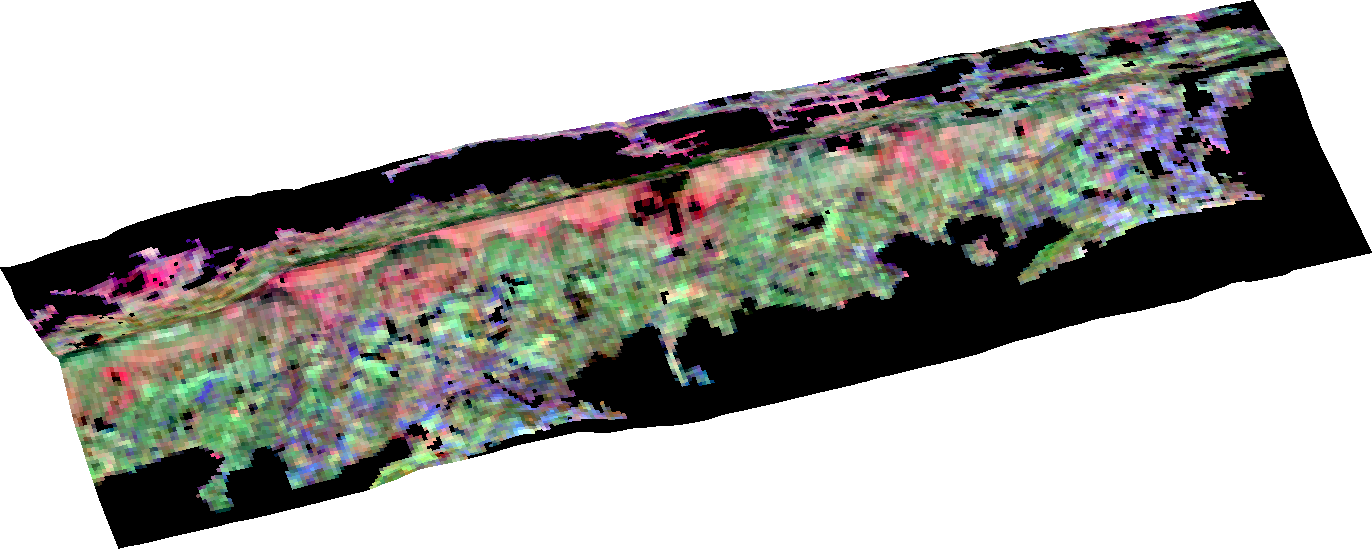
The advantages of satellite data are that they cover much larger areas than aerial measurements, provide regularly recurring observations of the same location, and cover remote areas. However, they have different sensor specifications, e.g., a coarser spatial resolution.
In my master thesis, I derived biochemical properties from the satellite data, for example, chlorophyll content and corresponding indices. In the next step, I compared these indices with those derived from the data recorded from airplanes. Thus, I was able to show how satellite data can be used for a large-scale measurement of functional diversity. The seasonal variability in traits and diversity variables also plays an important role, which is why I compared changes of these variables in July and September.
Using remote sensing to see the forest for the trees
The background of this research is that the human-made changes in nature are extensive and fast-moving. However, data collection on site is complex and costly. As a result, there is often a lack of continuous coverage in space and time, especially in regions that are difficult to access. Here, aerial photographs and satellite data play a unique role. They provide continuous data of large areas from above without having to cut through the forest and measure individual trees on site.
I continue this work in my Ph.D. studies at the GIUZ within the framework of the URPP "Global Change and Biodiversity" with the support of the NOMIS Foundation. If we can map functional diversity from space, we will also better understand how ecosystems function and the consequences of environmental changes. Satellite data are available worldwide. They are, therefore, a valuable data source for monitoring biodiversity loss over time.
Isabelle Helfenstein